Effects of PFAS on soil structure and function
Filling the gaps
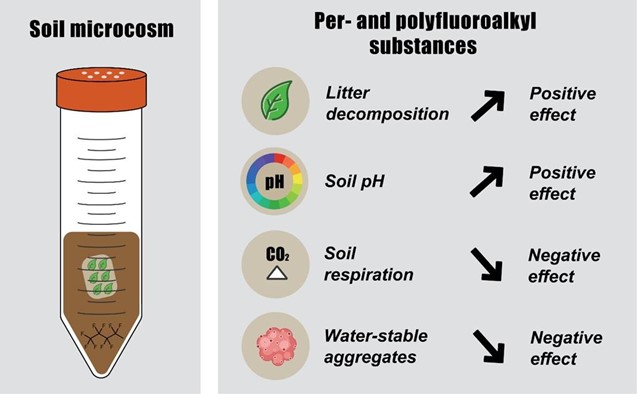
Among the chemical pollutants that are impacting soils globally, PFAS are of concern due to their high environmental persistence and as they might affect soil structure and function. However, data on impacts of PFAS on soil structure and microbially-driven processes are currently lacking. The study conducted by Dr. Baile Xu and his colleagues at Freie Universität Berlin explored the effects of PFOS, PFOA and PFBS at environmental-relevant concentrations on soil health, using a 6-week microcosm experiment.
The moment is now
One of the important findings of Dr. Xu's study is that PFAS significantly increased litter decomposition, even at 0.5 ng/g for PFBS. This probably means that -given their current environmental levels- PFAS present in soils now might already affect ecosystem processes.
Another eye-catching result is that the acidic PFAS significantly increased soil pH, instead of decreasing it. Dr. Xu and his team suppose that this was attributed to the direct consequence of increased litter decomposition, but not of PFAS. Additionally, PFAS also exerted detrimental impacts on soil respiration, microbial population and more importantly, soil water-stable aggregates.
Far-reaching consequences?
The finding that certain PFAS negatively affected water-stable aggregates could indicate far-reaching consequences for soil health, Dr. Xu concludes. Because of this, future studies need to explore these effects on the soil aggregation process in greater depth, including the formation, size distribution of soil aggregates and their intrinsic connections with soil biota.
More information: Baile Xu et al, Effects of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) on soil structure and function, Soil Ecology Letters (2022).
EmConSoil coordinator
- Adres
- Stationsstraat 110
2800 Mechelen
Route en bereikbaarheid - Telefoon
- +32 15 284 284
